School readiness diagnostic program
After discharge from the hospital, parents and the baby visits the patronage sister and the doctor. Medical workers control the overall condition of the child, follow the healing of the umbilical wound, assess the condition of the skin. Starting from the first month, parents need to independently bring the child to the polyclinic every month. This causes many questions from moms and dads: when to come, what to take with you, what to consult with the doctor and how there will be inspections.
In the clinics there is a special day of a healthy child, as a rule, this is Tuesday. Ask your doctor about it, since each clinic has its own traditions. Cannot come with the baby on other days. This risk pick up the virus. If the child is unhealthy, it is better to call a doctor to the house. Pediatricians take small patients on the coupons and for a common line. It is much more convenient to come with a coupon to a specific time, the ticket can be ordered on the Internet, by phone or take in the reception. It is worth postponing a visit to the clinic if the child has elevated temperatures, cough or you noticed that its overall state has deteriorated.

Internal intracranial pressure is all: both in adults, and in children, but its increase is considered a deviation from the norm.
Signs of increased intracranial pressure can be detected not only with the help of equipment.
Symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure
Parents should alert if the kid:
- throws off your head or sleeps with the head trapped back;
- at the age of several days confidently keeps his head (in the norm, this skill comes in 1-1.5 months);
So that the child grew up healthy

So that the child rose is healthy, the room where it is, you need to ventilate as often as possible. About once per hour. This disinfects the air and moisturizes it, and the baby gets the necessary oxygen dose. Thanks to this, he is less ill. Bedroom crumbs. Check the whole hour before bedtime.
Every day you need to walk on the street with any weather. Exception is a strong frost. But if the rain hoses or blows the wind, still go for a walk. The duration of staying on the street is the minimum of an hour. Do not wear a child too warm. He should not steam on a walk.
Power Mom after childbirth

Thanks to the special diet after childbirth, you can quickly restore the body, and not to gain extra kilograms that women are so afraid.
- From the first days after childbirth, and better and during pregnancy, eating wheat should be replaced with rye and corn bread. This will help a woman not to gain overweight, as well as avoid constipation and her, and baby.
- The amount of meat consumed should be reduced, fatty varieties are better to exclude in general from the diet.
- Milk must be replaced with cheese, cottage cheese or other fermented milk products. They contain enough calcium necessary to form a skeleton of a child and restoring mom's loss.
This program is a set of tasks and techniques to determine the differential level of readiness of children to school.
It is intended for individual work And it was designed to study children entering the first class. The diagnostic results were used to form classes with different, in terms of the level of complexity of training programs.
This technique allows you to assess the motivational readiness, level of speech development, learningability (mental or intellectual readiness), the ability to navigate in space, study some individual-psychological features of the child. It allows you to prevent the presence of deviations in the development of the cognitive sphere of the child before the beginning of the learning process.
Psychological and pedagogical readiness for school in this program is assessed by the formation of the following parameters:
- Motivational readiness is a positive attitude to school and teaching.
- Warely readiness is a rather high level of development of arbitrariness in behavior and intellectual activity, the ability to force themselves to do that it is difficult and not to do what I want.
- Mental readiness is the level of development of cognitive processes.
- Trainability as an opportunity to master a new way to solve problems and transfer a learned method for performing similar tasks.
- Speech development.
- The presence of a certain stock of knowledge and skills.
When performing diagnostic tasks, the child first notes the adoption of the task: methods for performing the task; learning in the survey process; Attitude to the result of its activities.
Task adoption - the consent of the child to fulfill the proposed tasks regardless of the quality of the fulfillment itself is the first absolutely necessary condition for the task. At the same time, the child shows an interest either to subjects used to present tasks (cubes, pictures, etc.), or to cognitive tasks.
Methods for performing the task: chaotic actions; Method of practical orientation - "method of samples and errors", a method of practical testing; The method of visual orientation.
The most primitive way is "action by force" or chaotic action without taking into account properties and quality of the subject.
Diagnostic learning. Many tasks in this program are offered to children in the form of a training experiment, that is, the child is trained to perform the task, and then the assimilation of the solution on the new similar problem is checked.
Child's attitude to the results of their activities.
The overwhelming majority of normally developing children show an active interest in the proposed tasks and the final result. For children with intelligence impairment, as a rule, an indifferent attitude to the tasks and the result obtained.
Help in the survey process
In the process of diagnosis, children are offered the following types of assistance:
Organizing help (o) - think more; do not rush; "Think by eyes - hands behind the back";
Learning assistance (y) - an explanation, action to imitate; using index gestures and speech instructions);
Emotional support (E) - "Well done", "You will succeed", etc.
The number of job appears should not exceed 2-3 times. At the same time, the speech of the adult should serve as a pointer to the goal of this task, the organization of a child actions and evaluating the effectiveness of its actions. The types and number of assistance provided are noted in the protocol.
The lack of training in the survey process can be associated with a rough reduction in intelligence or with violations in the emotional-volitional sphere.
Requirements for methods
Tasks and techniques in this program were selected by subsequent criteria:
- reliability;
- brevity;
- simplicity of results processing;
- variability, i.e. The presence of several equivalent options for assignments, to eliminate the "interlocking" by parents in the conditions of a flow of examination and the presence of several types of tasks of different levels of complexity;
- the understanding of tasks to parents and teachers;
- opportunity based on their development forecast.
Procedure for diagnostics
The procedure for holding tasks and methods are described in the Protocol
1. The conversation is held on the issues specified in the Protocol.
It is necessary to pay attention to the accuracy of answers to questions. The child responds with a full answer or monosyllant, willingly or the answers you have to pull out, the errors in speech are recorded. The content of the responses and the behavior of the child in the survey situation is also analyzed, to determine motivational readiness (game or educational) and personal characteristics of the child.
The score is directly not assessed, the task is included to create a child's sense of success and removal of anxiety.
The account in the reverse order is estimated on the tempo, the presence of errors.
The score in the specified boundaries is estimated according to the following parameters: the result, from which attempt can perform the task, how help uses whether to repeat the task.
If the child does not hold the boundaries of the interval, this indicates a low random child's memory.
If you repeat the task with distortion - about misunderstanding the instructions, reducing the understanding of the processed speech.
3. Task on the definition of the left and right hand.
The result is evaluated, the stability of the task execution than explains its choice.
4. Task.
When executing it is estimated: the result, understanding of the instruction, the ability to repeat the task, immediately says the answer or considers a finger (eyes) of cubes; Trainability (which attempt made the task, which types of assistance were used, the effectiveness of assistance, the sustainability of the result).
Material for task: 10 small cubes or circles or other small figures.
5. Slogging structure.
It is carried out if, when performing previous tasks, errors were detected in sound suspension, a distortion of the structure of words or violation of coordination was recorded. You need to repeat a few words 3-5. It is estimated to correct pronunciation, tempo, the ability to repeat in syllables.
6. Sound synthesis.
It is conducted in all subparagraphs if there are violations in speech. If there are no violations, start with 4 sounds, the rate of 4-5 sounds. Be sure to use diagnostic learning.
7. Sound analysis.
It is conducted in all subparagraphs if there are violations in speech. Must be used diagnostic learning if the child did not attend kindergarten and his school was not prepared
Methods for determining the level of thinking. The result is estimated (which signs allocate and how much), learning (from what attempt to fulfill the task), the types and volume of assistance rendered, its effectiveness, fulfillment of the task of speech instructions or a visual model, the stability of ownership of concepts color, size, form, correctness of using them in speech.
Tasks 8 * and 8 ** Increased difficulty levels are carried out if the child easily coped with the previous task.
Material for task. Eight cards with a picture of circles and squares of blue and red color of large and small.
(Big Blue Circle, Big Blue Square, Little Blue Circle, Little Blue Square, Big Red Circle, Big Red Square, Little Red Circle, Little Red Square )
9. Test of short-term memory and conclusion (Gilbuch Yu.Z.).
It is carried out if the child coped easily with the task 8, if he coped with difficulty or did not cope at all, go to the task 10.
Estimated:
The level of memory development (with what attempt I remember the task);
The result of the execution (independently; with the help of visual support, in parts);
Resistant results.
10. Drawing up a story on a consistent row of pictures.
The complexity of the task (out of 3, out of 4, out of 5 or from 6-pictures, the child will be a story) is determined by the results of the previous tasks, the higher the result, the greater the pictures.
Estimated:
Correctness of laying pictures by parameters specified in the protocol;
Compiled story.
Material for task. Sets of plot pictures of 3, 4, 5, 6 pictures from any diagnostic psychological or speech therapy examination.
Assessment of tasks
When performing tasks with a child, a teacher or psychologist conducts a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the execution of each task. A qualitative assessment is carried out by parameters specified in the previous section and the criteria that are specified in the Protocol. The corresponding execution is emphasized or shown in it with a handle. If necessary, comments are added on the fields.
Quantitative assessment:
0 points are put if the child refuses to perform the task and it fails to persuade it.
1 score - the child proceeds to perform the task, but does not understand the conditions of the problem even after training; It behaves inadequately in relation to the methods of action in this task, does not allocate its goals.
2 points - the child takes a task, begins to perform it, but independently does not reach the goal, in the process of diagnostic learning, it acts adequately, but after training does not pass to independent fulfillment of the task;
3 points - the child accepted and understood the conditions of the task, but when it was fulfilled, it relies on a low orientation, after training, it becomes a higher type of indicative activity, interested in the final result;
4 points - the child immediately understands and accepts the conditions of the problem, independently uses adequate ways of orientation when executed it, seeks a positive result.
High levels - tasks are performed by 3-4.
Middle level - tasks are performed by 2-3.
Low level - tasks are performed by 1-2.
After the diagnostic program is fulfilled, a psychologist with a teacher gives a quantitative assessment of all tasks. After that, it is written about the level of readiness for school.
Conducting diagnostics from 15 to 30 min. Multivariates of the tasks of this technique make it possible to use it if necessary for repeatedsurveys. This technique was used by me for 15 years to form multi-level classes.
Children's readiness diagnostic protocol for school education
Name your surname, name, patronymic.
When's your birthday?
Surname_________________________
Name_________________
Middle name_________________________
Date of Birth________
Did you go to kindergarten ______________________
What did you like in kindergarten? ___________________
Was something in d / s, what didn't you like? _______
Want to go to school? What can you do? _______
There are: accuracy of answers; violation of sound suspension;
single responses; motivation.
Calculate:
from 3 to 7 1); 2); 3); four)
from 9 to 4 1); 2); 3); four)
Noted: skip, slow down the tempo, the ability to repeat the task.
3. Task for the definition of the left and right hand
(Raise) left hand.
left hand right eye
right hand left ear
my left hand
4. Task.
Instruction.
Put on the left side of 5 cubes, and with the right to 1 cube more. How much?
I shift from the left column in the right 1 cube.
Where else?
How much more?
5. Slot structure
Repeat difficult words:
distort rate. By syllables in any way
Pan,
Transport,
Policeman
Scuba
Thermometer.
6. Sound synthesis
Guess what word I say? Example: d * o * m * - house; M * A * K - Mac. The word is pronounced by sounds.
| MOUTH | 1) | 2) | |||
| LESSON | 1) | 2) | |||
| TABLE | 1) | 2) | 3) | ||
| TANK | 1) | 2) | 3) | ||
| PINE | 1) | 2) | 3) | 4) | 5) |
Noted: What attempt the task correctly
7. Sound analysis
And now you tell me the sounds. Example: Nose - H * O * C *; Table - C * T * O * L *
Spider, stork,
Duck, Cross, Pattern
Sofa, boot, handle
There are permits, permutations, with what attempt correctly completed the task.
In front of the child, all eight cards depicting circles and squares are laid out.
I choose this figure, and you choose from the remaining figure most unlike my.
Tell me, what do they dislike?
If the child quickly and easily coped with the previous task, it is offered tasks 8 * and 8 **. If a lot of difficulties have arisen when learning, we immediately go to the execution of the task 10.
eight*. - Choose 2 figures that are unlike (they are different) only:
Size
eight**. - Choose 2 figures that are similar (they have the same) only:
Size
9. Test short-term memory and conclusion. (Gilbuch Yu.Z.)
Remember the task.
"There were three girls Masha, Olya and Katya. Masha above Oli, Olya above Kati. "
Options.
"There were three girls. Anya, Valya and Galya. Anya below Vali, Valya below Gali.
"There were three boys. Sasha, Kolya and Peter. Sasha above Kolya, Kohl is above Pet. "
"There were three boys. Seryozha, Vitya and Mitya. Seryozha below Vitia, Vitya below Mitya.
Repeat.
The number of repetitions of the required child to memorize the task are noted. If necessary, the task is repeated in parts.
Well done! Now you repeated right. And now think and say.
Which of them is the highest?
Who is the lowest?
Who is medium height?
There are: independently executed, help with a visual support, in parts, in no way.
10. Drawing up a story on a consistent row of pictures. (3 cards, 4 cards, 5 cards or 6 cards)
In front of the child, all cards are unfolded.
Instruction . Spread pictures in order and make up the story.
It is noted: decomposed independently, quickly, slowly, with help, laid a psychologist.
independent______________________________
On issues?
Answers questions: right - incorrectly, deployed - monosyllant.
Errors ____________________________________
Suggestions:
non-proliferated
common
complexed
If it is necessary to assess the development of visual and motor coordination, the child is proposed to continue the simple graphic pattern.
Instruction. Consider carefully and continue the pattern.
Estimated: Hold the sequence of elements, compound, height stability, error correction.
Conclusion ______________________________.
Important place in educational process belongs to the diagnosis, the readiness of children to school learningwhich allows an adult to understand whether the direction is correct, he is preparing children to school. Diagnostics reveals the causes of the child's promotion to a higher level of development.
Download:
Preview:
School readiness diagnostic program
An important place in the educational process belongs to the diagnosis, the readiness of children to school, which allows the adult to understand whether the direction is in the right direction, he prepares children to school. Diagnostics reveals the causes of the child's promotion to a higher level of development.
Readiness for school learning is made up of many components:
1. Physical readiness for school is determined by the physical development of the child and its correspondence age standards, that is, the child must achieve the physical maturity necessary for the educational process.
2. Psychological readiness for the school implies a certain level of formation: general awareness and social orientation; knowledge and ideas about the world around; mental operations, actions and skills; arbitrary regulation of activity and behavior; cognitive activity manifested in appropriate interest and motivation; Speech Development, involving possession of a fairly extensive dictionary, the foundations of the grammatical system of speech, a connected statement and elements of monologue speech.
3. Emotional maturity is the ability to regulate its behavior, which includes the ability to perform a long time to perform a very attractive task.
4. Socio-communicative readiness for school develops from the abilities of a child to build relationships in the team of peers: hold a leading position, be able to work in a team and maintain the leader - and also be able to communicate with an adult interlocutor.
Technique. Test Core-Irashka.
Kerna Ya. Yirasek chose three tasks: drawing a male figure, imitating writing letters and handling a group of points. All three tasks of this test are graphic and are aimed at determining the development of fine motility hands and visual and engine coordination.
Test tasks are performed by the test on instructions and sample. The test can be applied individually and in the group. The execution of each task is estimated according to the five-point system (1 - the highest score, 5 - the lowest), and then the total result is calculated in all tasks
"Figure Male Figure."
Estractions: "Draw some man."
Data processing Evaluation of the test execution (marks from 1 to 5) goes for each task separately.
Task 1. Drawing of a male figure (key). 1 score - drawn figure should have a head, torso and limb. Head with a torso is connected by neck, and it is no more torso. There are hair on his head (or their arm and hat are finished) and ears, on the face of the eye, nose and mouth. Hands are finished with brushes, on each - five fingers. Legs downstairs bent. Man's clothes. The figure is drawn using the so-called synthetic method.
2 points - execution of all requirements, as in paragraph 1, except for the synthetic image method. Three missing parts (neck, hair, one finger, but not part of the face) can be turned off from the requirements if it is backed by a synthetic image of the image.
3 points - the drawing should have a head, torso and limb. Hands or legs are drawn by a double line. It is allowed the absence of neck, ears, hair, clothes, fingers and feet.
4 points - primitive drawing with a torso. The limbs (enough single pair) are expressed only by simple lines.
5 points - there is not enough clear image of the body ("head-like" image or overcoming a "pinchot" image) or both limbs. Below are samples to estimate the test of the test.
"Imitation with written letters"
Instruction: "Look, something is written here. You have not yet learned to write, but try, maybe you will also be able to. Look carefully how it is written, and near (right) on an empty place write the same
1 score is completely satisfactory (in the sense of reading) imitation of the written sample. The initial letter has a noticeable height of a capital letter. Letters are well connected in two words. A rewritten proposal does not deviate from the horizontal line by more than 30 °.
2 points - a fairly legitimate imitation of the written sentence. The value of letters and respect for horizontalism are not taken into account.
3 points - obviously dismemberment is minimal into two parts. You can disassemble at least four sample letters.
4 points - the sample looks like at least two letters. The whole still forms the line of "Scriptures".
5 points - Drawing
"Sourcing a group of points"
Instructions: "Look, drew points here. Try and draw nearby in the same way. "
1 point - almost perfect imitation sample. We only admit a very small deviation of one point from a number or column. The decrease in the figure is unacceptable, the increase should not be more than half. The drawing must be parallel with the sample.
2 points - the number and location of the points should respond the sample. You can deviate even three points per half of the rows or columns.
3 points - an integer in its contour looks like a sample. In height and width, it does not exceed it more than twice. The points should not be in the right number, but there should be no more than twenty or less than seven. Any pivot is allowed - even 180 °.
4 points - the drawing in the contour is no longer similar to the sample, but it still consists of points. The magnitude of the pattern and the number of points do not matter. Other forms (lines) are not allowed.
5 points - Drawing
12-15 points - ready to learn at school 9-11 points - Conditionally ready 3-6 points - not ready
Methodology 2. "Doringing figures"
The purpose of the methodology: a study of the development of imagination Children is given by 10 figures (see the application to the method No. 2) and is offered, reflection, trying these figures, so that it turns out the picture. Pictures are estimated on a ten-ball scale. Rating: 0-2 points - the child did not invent anything; Drew something nearby; Uncertain strokes and lines.
3-4 points - painted something simple, non-original, deprived of details; Fantasy is not guessed.
5-7 points - depicted a separate object, but with a variety of additions.
8-9 points - drew several objects united by the plot.
10 points - created a single composition by including all the items proposed in it turned into images
Key 8 - 10 points - ready to study at school 3 - 7 points - conditionally ready 0-2 points - not ready
"Spatial-arithmetic dictation".
This task allows you to diagnose both the formation of account skills and some psychological characteristics: the child's ability to navigate in space (right-left, top-bottom), the ability to act according to the rules, understand the oral instructions and keep it in memory.
Next, the child is asked the following questions: 1. If it will go from his cell to the right on one cell, then where will it be? What will she find there? How many? 2. Next, it will also take up one cell from this cell. Where will it be? How much did carrots become hot now? 3. Now it goes to one cell to the left. Where will she be now? How much is carrots now? 4. The girl is still on one cell left. Where will it be now? Here, the bunny asked her 2 carrots. How much does it have left? 5. She is still on one cell down. Where will it be? How much is carrots now? Did anything change? 6. The girl goes down. Who did she meet? She gives her 2 carrots. How much does it have? If on the first questions, the teacher sees that the child does not respond to them and can not answer, and at the same time there are suspicions that he just did not understand the instructions or too clamped, then he can solve the child with a finger to move on the table For instructions. The teacher itself does not show anything. Evaluation Criteria: 2 points - ready to study at school. The child performed 5-6 actions from 6 possible.
1 point is conditionally ready. The child correctly performed 3-4 actions of 6 possible. 0 points - not ready. The child performed the correct 1-2 actions of 6 possible.
"Sequential pictures"
This test allows you to identify the level of sprinkling the child of causal, spatial-temporal, logical connections, as well as the level of development of monologic speech (the ability to build a connected serial story). Instruction: A common card with stimulus material must be cut into parts and, mixing them, put them in front of a child with the words: "I have pictures (see Appendix No. 8). They are all confused. Try to decompose them in order in front of yourself on the table, and then tell me some story (make a story) "
2 points - ready to study at school. The child independently and logically determines the sequence of pictures and makes a connected story;
1 point is conditionally ready. The child is mistaken in the sequence, but corrects it (himself or with the help of an adult) or if the story is fragmentary and causes difficulties in a child;
0 points - not ready. The child violates the sequence, can not understand the mistakes or his story comes down to the description of the individual details of the pictures.
Diagnosis of the level of development of arbitrary attention and arbitrary memory.
Purpose: to identify the number of conditions that the child can keep in the process of activity at the perception of a rumor task. Description: The task is performed on separate sheets. For each child, each child should have a graphics pencil and a set of color pencils. The child is proposed to draw a certain number of triangles into a row, some of them need to shake the color specified by adults. Repeat task is categorically prohibited. If the child did not remember, let him do in his own way
instruction: "Now we will play. Pay attention. I will explain the task only once. Draw in a number of 10 triangles. Sharchui with a red pencil third, seventh and ninth triangles. " The test conditions are pronounced at a slow pace, each condition is allocated by voice. Assessment of completed task: 5 points - the task is made correctly, all conditions are taken into account: form geometric Figure, their quantity, selected pencil color, sequence of shaded figures
4 points - one error is allowed.
3 points - two errors are allowed.
2 points - three errors are allowed.
1 score - more than three errors
0 points - I did not cope with the task.
Key: 5 points - ready to study at school
3 - 4 points - conditionally ready
0-2 points - not ready
"Analogs".
Purpose: The task is directed to the study of thinking, namely, it allows you to see the degree of formation of a child's ability to make conclusions by analogy. Instruction: "I will call you three words. Two of them are suitable for each other, are a pair. You will need to come up with a word suitable for the meaning to T2 points - the child found the right word in 5-6 cases out of 6 possible.
1 point - the child found the right word in 3-4 cases out of 6 possible.
0 points - the child found the right word in 1-2 cases out of 6 possible. Key: 2 points - Ready for school training;
1 score - conditionally ready for school training;
0 points - not ready to study at school
By the third word, that is, to find him a couple. The words are: - Okun - Fish, and chamomile - ...? (Flower) - Carrot - Garden, and mushrooms - ... (forest) - hours - time, and a thermometer - ...? (Temperature) - Eyes - Vision, and ears - ...? (rumor) - good - evil, and day - ...? (night) - iron, and the phone is ...? (call)
Methods "Riding on tracks"
Material: Drawing Option, Pencil
Instruction: "Let's imagine that you are a driver and you need to drive up here to this house (so far in version b)." At the same option, I draw, explaining: "You will go like this: the pencil should not serve from paper, otherwise it turns out that the car took off. Try to go carefully, so that Ma-tire does not move from the road. "
Final level:
High - there is no way out of the road, the pencil breaks away from paper for no more than 3 times;
Low - 3 or more outputs outside the road or an uneven, trembling line, very weak, invisible, or on the contrary, very strong push, taking paper and multiple it in the same place;
Middle - all other options.
Large movements
The level of development is checked to perform a set of exercises:
Go through a line 2-3 meters a heel to the sock;
Stand on the left foot, the right leg is adjusted, the eyes are closed. Can be balanced by hand. Rate of 15 seconds;
A child at a distance of 3-4 meters catches a little ball and throws back (6-7 shots).
Final level:
Inspective: 1) uneven gait; 2) the presence of a large number of movements that are accompanied by the main task and interfere with its implementation; 3) Violation of coordination: the child can not catch the ball, keep it or throw it back.
Sufficient - separate minor violations of the instructions when performing tasks.
Methodology "Labyrinth"
Purpose: Determination of the level of development of visual-shaped thinking.
The child needs to find the way to a certain house among others, the wrong, paths and dead end of the labyrinth. In this, it is helped by shaped specified instructions - by what objects (trees, bushes, colors, mushrooms) it will pass. The child must navigate in the labyrinth itself and the scheme. reflecting the sequence of the path steps.
Method "Two houses"
Purpose: to determine the circle of significant child communication, the features of relationships in the group, identifying sympathy for members. Diagnosis of interpersonal relationships of preschool children.
Instructions: "Look at these houses. Imagine that the red house belongs to you, there are many beautiful toys in it, and you can invite everyone to yourself. And in the black house there is no toys at all. Think and tell me who of the guys of their group would you invite to themselves, and whom she settled in a black house. "
Method "Secret"
Purpose: identification of the situation (sociometric status) of the child in the group of kindergarten, his attitudes towards children, as well as ideas about the attitude of peers towards him; The degree of benevolence of children to each other, their emotional well-being.
Instructions: Today, all children of your group secret, so that no one else knows about it, give each other pictures (toys). Here on the table lie pictures (toys) that you can give. And other children will give you, because today everyone is given to each other. Do you want to give pictures (toys) to children of your group? (Having received a positive answer, the adult continues). Then choose, please picture (toy), which you like best. Who among your group children do you want to give her? Why?
Method "Pictogram"
Purpose: study of the singularities of indirect memorization and its productivity, as well as the nature of mental activity, the level of formation of conceptual thinking. The technique can be used to study children and adults in group and individual examination. Material: Pure Paper Sheet, One Simple or Several Color Pencils, Word Set
Instruction (option for children): "Now we will check your memory. I will call you words, and you draw a picture for each word, for which you can remember this word
Method Color Test Lucher
Purpose: The color diagnosis of the lasuscher allows you to measure the psycho-physiological state of the person, its stress resistance, activity and communicative abilities. The Test of Lucher allows to determine the causes of psychological stress, which can lead to the emergence of physiological symptoms.
Test "Figure School"
Purpose: definition of a child's relationship to school and school anxiety.
The child is given a sheet A4, color pencils and ask: "Here on a sheet of paper, draw school."
Conversation clarifying questions about drawn, comments are written on the back of the picture.
Processing results
Emotional attitude to school and teaching is estimated at 3 indicators:
1) color gamut;
2) line and character pattern;
3) Picture plot.
When analyzing the pattern for each of these indicators, a score assessment is exhibited, then the points are folded.
1) Color range:
2 points - in the figure prevail bright, clean, light tones and their combinations (yellow, light green, blue, etc.)
0 points - the drawing is made in dark colors (dark brown, dark green, black).
1 point - equally present bright and dark tones.
2) Line and character pattern:
2 points - objects are drawn carefully and neatly; Long, complex lines of different thicknesses are used, no "breaks" of the contour.
0 points - objects are shown deliberately carelessly, schematically; Double lines, interrupted, equal length and thickness, weak line.
1 point - in the picture there are both characteristics.
3) Picture plot:
2 points - a symmetrical image (the school drawing occupies a central place on the sheet); The presence of details and decorations, decoration elements, image of various items, animated landscape (flowers, trees, posters, flags, curtains on the windows, etc.); An image of children going to school or sitting at the parties, teachers and the "teaching process"; season - Spring, summer (sun, no clouds); An image of a light day of day.
0 points - asymmetry drawing; lack of details and decorations; lack of people or image of children leaving school; season - autumn, winter (dark sky, it is raining or snow); Time of day - night or evening.
1 score - both characteristics are present.
Analysis of the results
6-5 points - the child has an emotionally prosperous attitude towards school and teaching, it is ready for the adoption of educational tasks and interacting with the teacher.
4-2 points - the child has some anxiety about school learning as an unfamiliar situation for him, it is necessary to expand the range of his knowledge and ideas about schoolboy learning activities, form a positive attitude to the teacher and classmates; The reasons of anxiety may be nervousness and rapid statements of adults, negative learning experience in the school of older children.
1-0 points - a child has a clear fear of school, often it leads to the rejection of educational tasks and the abandonment of training activities, difficulties in communicating with the teacher and classmates.
"Knowledge of color" (task)
In front of the child puts the chalkboard with 12 colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue, purple, pink, black, gray, white, brown) and alternately, in any order they offer him to call one or another color.
Quest Evaluation: For each correctly called color 1 point is accrued
"Knowledge of object names." (the task)
In front of the child lay out 9 of any pictures: apple, carrots, rose, pear, tulip, cabbage, sunflower, cherry, carnation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Then ask to call every item. When answering, for example, "this flower" is asked to clarify which one. If the child calls the items incorrectly, the researcher at the end of the task should correct its errors.
Quest Evaluation: Each correct answer is estimated at one point.
"Account order." (the task)
All children who coped with the fifth task are asked: "Consider in order how much you can." If the child does not understand the tasks, the researcher helps him: "1, 2, 3 ...". Then the child is offered to start independently first. With the termination of the account, the researcher says: "That's right, what is the number further?" Next, 22 is not necessary.
Quest Evaluation:
As an estimate, the number is set to which the child correctly counted.
"Color and Form Differentiation." (the task)
Before the child, lay a sheet of paper with drawings of unfinished figures
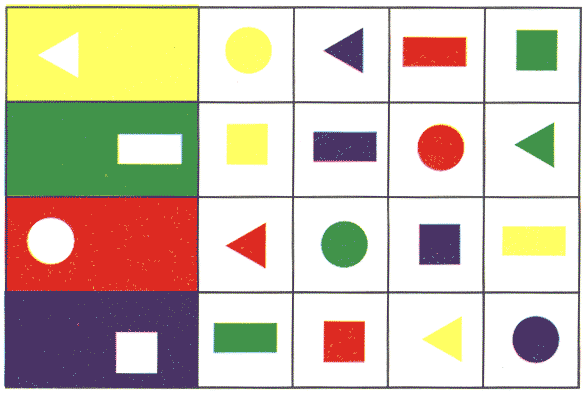
Instruction: "Rectangles (show) are drawn here. Each of them lacks a piece (show). Pick up for each rectangle a suitable piece of all drawn here (show). Look, what kind of piece comes to this rectangle (show the first figure)? "
Then they are consistently shown on the other pieces, with a request to choose the missing parts to them.
Quest Evaluation: Each proper decision should be estimated at one point.
"Description of the picture." (the task)
Child show a picture 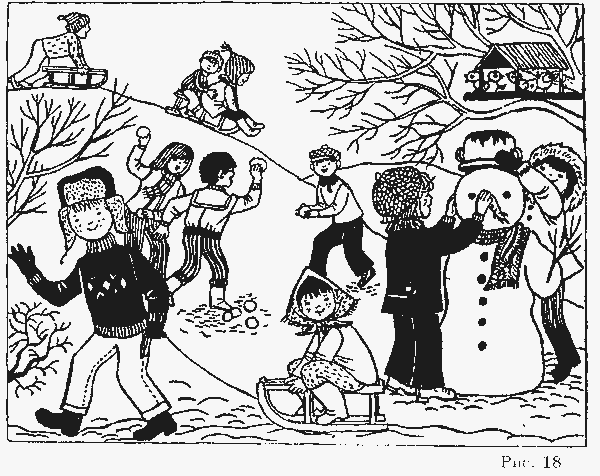
and they say: "Tell me, please, what happens in the picture (Fig. 18)."
Quest Evaluation:
a) conversational speech.
2 points - fluent speech without hoist
1 score is a quick speech, but there are pauses.
0 points - Speech stuffing, interrupted.
b) Building proposals.
8 points are well-structured complex suggestions, connective alliances are used.
6 points - Complex sentences, One union is stereotypically used.
4 points - mainly simple sentences.
1 point is predominantly incomplete sentences.
0 points - the construction of proposals is violated.
c) Articulation.
2 points - a clear pronunciation of sounds.
1 score is a fuzzy sound pronunciation.
d) fantasy, imagination.
It is estimated at 1 point if the child does not simply tell about what is depicted in the picture, but also about the experiences, thoughts of heroes, specifies that there was or will be, etc.
Thus, the maximum score throughout the task 13 points.
Chebykina Natalia Borisovna
School readiness diagnostic program
Exercise 1
Purpose. Release the ability to transmit the shape of the shape (draw an equal or similar figure, observing the proportion between the elements of the figure). In addition, the task allows you to judge the hardness of the child's hand, the ability to draw the angles, without growing them, and rectilinear segments.
Test text. "Look here (indicates the drawing to the task ). Here you will do the task. Inside a small frame you see the shape. Consider it. Take a pencil. Draw a similar figure in a big frame "(teacher Classes Pointer A Large Framework ).
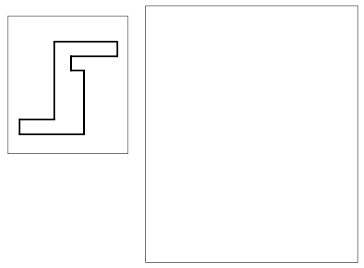
Task Performance Assessment:
0 points
- not captured the general form of the figure, but some closed line is depicted;
1 point
- significantly changed the proportions between the elements of the figure; The total shape of the figure is silent badly;
2 points
- depicts a similar or equal figure, the proportions are slightly changed, but not all the corners are direct, the parallelism of the lines is observed everywhere. The same score is placed if the total shape of the figure is cleaned well, but the proportions between the elements of the figure are substantially changed, but all the corners are direct and parallelism is observed;
3 points
- depicts a similar or equal figure, the proportions between the elements of the shape are mainly stored.
If the figure is depicted with a non-solid hand, in addition to the score, the "minus" sign is put.
Task 2.
Purpose. Review the ability to navigate on the plane (left, right, up, down). The ability to recalculate cells is also checked.
Test text. "Task you will perform on the checkered part of your sheet (indicates a place to perform a task ). Find a black cell on the checkest field.
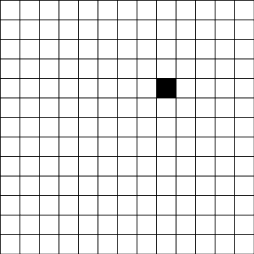
1. Take a red pencil, referring to the black cell to the right four cells and the fifth of the red pencil.
2. Take the blue pencil. From the Red Cell, retreating down two cells and fed the third pencil.
3. Take the green pencil and the cell, located on the left of the blue, through one cell from it, flooding with a green pencil.
4. Take a yellow pencil. Count the green cell up five cells and the sixth filtering with a yellow pencil. "
Task Performance Assessment:
0 points
- the student did not start fulfilling the task; Several cells are painted, but their location does not correspond to the instruction;
1 point
- only one task item is executed true, errors are made in the direction, recalculate the cells, the beginning of the reference;
2 points
- the 2-3 point of the task is fulfilled;
3 points
- All task items are fulfilled.
If the cells are poorly painted, in addition to the score, the "minus" sign is put.
Task 3.
Purpose. To identify the skills to select and perform the operation of addition and subtraction, to correctly understand the text of the task and move from the specified number to the corresponding final set of items (circles, squares).
Test text. "Here you will do the third task (indicates a place to perform task 3 ). Listen to the task.
1. In the class (group) today, 3 girls and 2 boys are on duty. How many children are on duty today in class? Draw as many circles as children on duty today in class. (Task text can be repeated .)
2. 6 people drove in a passenger car. Two came out of the car. Draw as many squares as people remained in the car. (Task text can be repeated )».
Task Performance Assessment:
0 points
- there is an attempt to solve one task, but the number of circles or squares is incorrect;
1 point
- only one task is true, there is no attempt to perform the second task;
2 points
- one task is true, there is an attempt to solve the second task, but the number of circles or squares is incorrect;
3 points
- Both tasks are fulfilled.
Task 4.
Purpose. Release the ability to compare the set by the number of elements (regardless of the account skill).
Test text. "Find on your sheets in the articles, on which circles and triangles are depicted (indicated drawing to task 4 ). What is more: circles or triangles? If more circles, then draw another circle next. If more triangles, then draw another triangle. "
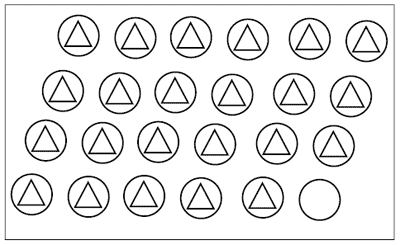
Task Performance Assessment:
0 points
- comparison was carried out incorrectly (one triangle was drawn);
3 points
- Comparison is done correctly (one circle is drawn).
Task 5.
Purpose. Release the ability to classify, find the signs for which the classification is made.
Test text. "Consider these two drawings (points to task 5 ). On one of these drawings, you need to draw a protein. Think on what picture you would draw it. From the protein to this drawing, spend a pencil line. "
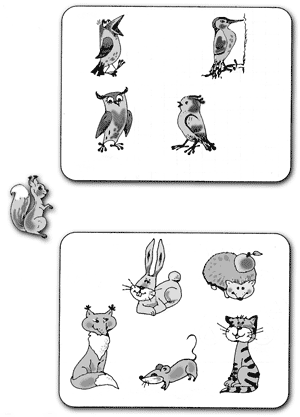
Task Performance Assessment:
0 points
- The task is not accepted, the line has not been carried out;
1 point
- the line was carried out incorrectly;
3 points
- The line is carried out correctly.
Task 6.
Purpose. Check the state of phonmematic hearing, phonderatic perception in the process of selecting pictures with a given sound in their names.
Test text. "Look at these pictures. See, under them there are small circles. You need to independently call each picture and, if in the title of the picture there is a sound [s], cross the circle under it. In the first picture - the sun. In a wordthe sun There is a sound [C], then you need to starve a circle. And now proceed to an independent task execution. "
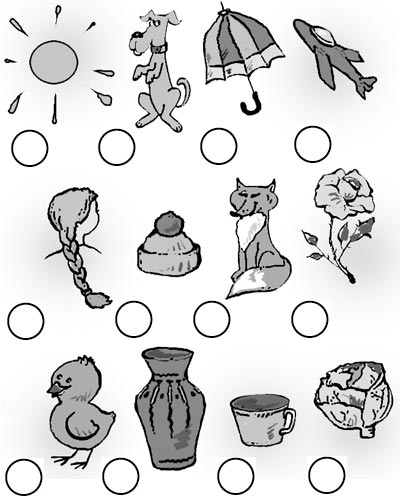

Estimation:
0 points
- the absence of differentiation of sounds [s] - [s], [s] - [C], [s] - [sh] or complete failure of the task;
1 point
- the presence of errors (there is no differentiation of sounds [s] - [z]);
2 points
- the sound is highlighted only from the position of the beginning of the word, the erroneous allocation of other sounds is not;
3 points
Task 7.
Purpose. To identify the degree of mastering by sound analysis at the level of determining the number of sounds in the word.
Test text. "You see the lodge with three windows and next to it are pictures. Each window is the sound in the word. Nazi quietly all pictures and think about three sounds. This picture connect the arrow with a house. "

Estimation:
0 points
- the complete absence of compliance with the number of sounds in the word and the number of "windows";
2 points
- the presence of errors in one sound (the word is markedwolf
);
3 points
- Proper task execution.
Test material - knowledge of information about yourself, your family.
Call your last name, name, patronymic.
Name the surname, name, patronymic of Pope, Mom.
Who does your mom work (dad)?
Where do you live, call your home address?
Survey blank.
Surname name
School readiness
Total
points
Determining the type of orientation in relation to school and teaching (the level of formation of the child's internal position of the student) adapted standard conversation T.A. Tender Interpretation of the content of responses and evaluation criteria. A - orientation on the content of training activities ( 2 points);
B - orientation to the external attributes of school life ( 1 point);
In - orientation for out-of-school activities ( 0 points).
Questions
Content of answers
Point
1. Do you want to go to school?
And - I really want
B - so-so, I do not know
In - I do not want
2. Why do you want to go to school?
B - like new form, books, handles, pencils, briefcase, etc.
In the kindergarten in the kindergarten, they do not sleep at school, there are fun, all the children go to school, Mom said, etc.
3. Are you preparing for school? How are you preparing (how do you cook) to school?
And - I am engaged in the preparation group, we teach the letters with my mother, solve the tasks, etc.
B - I bought a form, school supplies, etc.
IN ( mentions school classes)
4. If you did not have to go to school and in kindergarten, what would you do at home, how did you spend your day?
And - wrote (a) letters, read (a), etc.
B - painted (a), loined (a), designed (a), etc.
B - played (a), walked (a), helped (a) at home, courted (a) for animals
Result
7-8 points - the internal position of the schoolchildren is sufficiently formed;
4-6 points - the initial stage of forming the internal position of the student;
0-3 points - The internal position of the schoolchildren is not formed.
With parents, it is necessary to discuss the results of the conversation, give recommendations.















