Optional strategies: classification by parameters. Basic optional strategies
Optional strategy - The powerful investment tool in which is not one base, but a group of options. Some strategies are "diluted" by the basic asset (for example, securities). Today there are many combinations that make transactions with different risks and to solve various tasks. Unlike standard assets transactions, optional strategies allow to obtain income even with minimal market volatility.
Optional strategy - Combination of options of different types that have different parameters and properties. With the right choice of strategy, it can use for earnings any time gap, maximally limiting their risks. When considering option strategies, one of the main parameters is the "break-even level" ("point of payback"). The optional strategy is a basic (simple) and complex, depending on the toolkit used.
Optional Strategy: Basic (Simple) Options
Standard (simple) optional strategies are characterized by a minimum set of tools and availability even for beginner investors. The most popular strategies for this class include:
1. Capped "Call" or "Put" options.
The coating strategy is good for its simplicity. The best time for use is periods of irrelevant market activity (minimum volatility). With proper use, you can count on an additional one by open positions. The essence is on the sale of the Call option with an existing position with the PUT option.
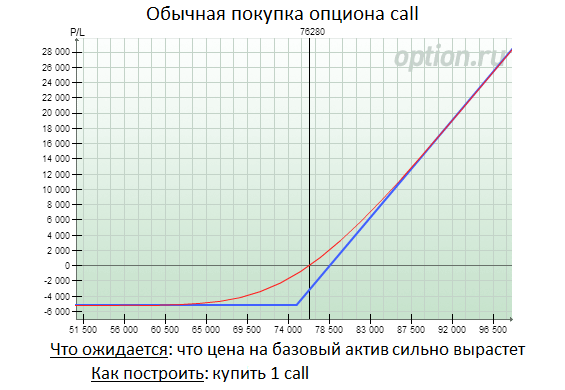
For example, an investor bought one lot of Apple for $ 30. But the price of the asset price after purchase ceased or became too "slugged". In such a situation, you can sell for the shares of this company with the cost of execution of 35 dollars. If the cost of the contract for this will be below 35 dollars, it will have to be supplied at a cost of $ 35. At the same time, from part of cash on cash will have to refuse.
The feature of the strategy is the ability to increase cash returns and reduce current risks. If the price crawls below 30 dollars, then the options will not be executed, and the profit will cover the loss from falling prices.
The essence of such an optional strategy is to buy Call and Put contracts with identical price and execution time (final expiration period). The use of strodel is relevant in the case when a powerful price change is expected (up or down). The calculation is based on what will make money on any of the options. Consider the situation. The price of an asset of interest has long been "hanging" at 50-60 dollars. At the same time, future events allow us to talk about a sharp change price through time. In such a situation, you can use the strategy strategy and arrange PUT and CALL with a price of 55.
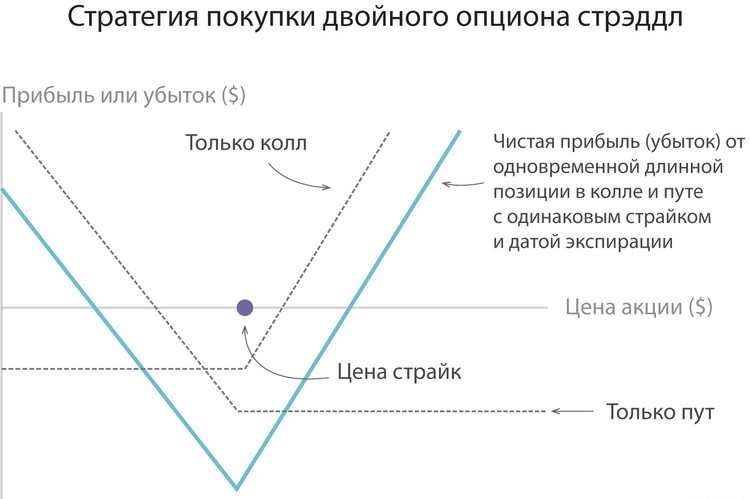
The feature of the system is in the presence of two break-even points. For example, if the size of the award is 2 dollars, then you can count on profit when the cost parameter is outputting for the conditional limits (below 51 and above 59). It does not matter what the price goes out of the destinations.
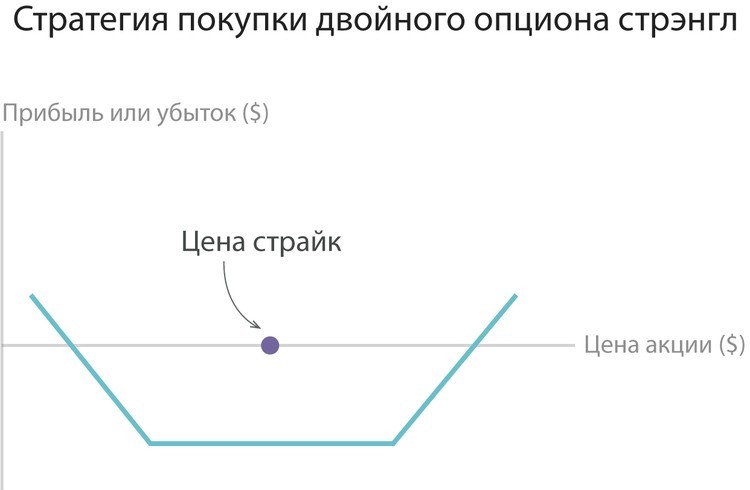
3. Strangl.
This strategy is a more affordable and cheap version of Stradela. It is based on Call and Put options that have various strikes and identical expiration time. This approach allows you to make break-even zones wider for the investor. If we consider the past example, the investor could save on the board for and buy two contracts by 53 and 57 dollars. If the award is equal to one dollar for 57 Call option and two dollars for the 53 optional option, then you can count on profits at a price - from 50 to $ 60.
4. Bear and bullish.
The most simple are Bear Spread and Bull Spread. Such strategies are often called vertical.
The essence of bovine spredes - In buying a Call contract and selling the same asset, but already with a big strike. For example, at a price of $ 50 for an asset, an investor awaits price growth to a level of $ 60, but not more than $ 70. Here is the optimal Call spread "Bull" - 55-70 dollars. By paying a premium in the amount of five dollars for a purchased 55 Call, as well as receiving an optional price of $ 3 for 70 PUT, you can get a net value of the option (income) in the amount of two dollars. At the same time, the break-even point will be at the level of 57 dollars.
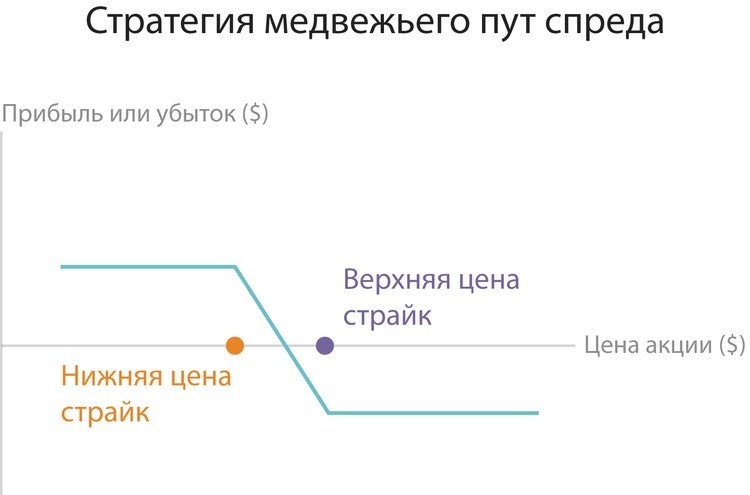
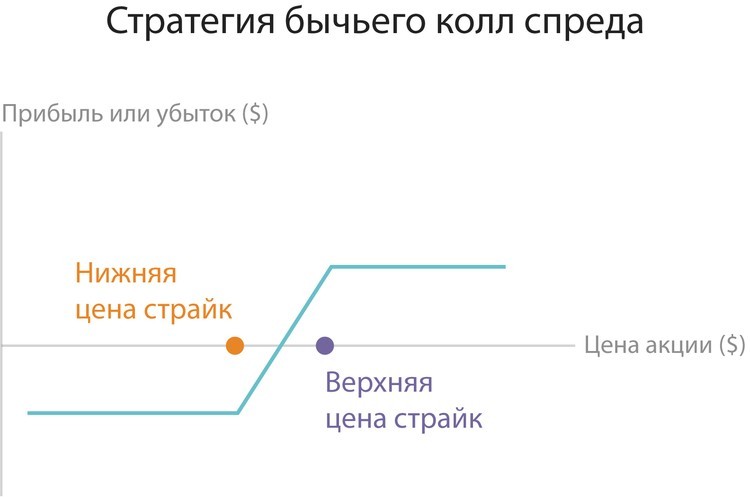
The principle of the spread of a bearish type is similar. The difference is only in changing the direction of movement.
5. Range forward.
This type of optional strategy is in demand among major market participants - banking structures and investment enterprises. The strategy is based on several instruments - sold and purchased PUT or CALL options that have identical validity periods (expiration date) and strikes.
The "Ranband Forward" strategy showed itself when hedging risks in the event of a sharp decline in the exchange rate. If the bank wants to eliminate the risks from reducing the total price to the US dollar, for example, on 20 million euros, then the purchase of PUT options on the European currency and the sale of the Call option on the same monetary unit will fix the price.
The strategy is good for hedgers, because the purchase of option contracts at least partially (with adverse movement) is covered by the implementation of option contracts with favorable price change.
Optional strategies: complex options
In the practice of optional trade there are more complex strategies to which:
1. Calendar Sprord.
Many specialists note the similarity of this strategy with an ordinary bull. The difference is the presence of one value of execution, but different dates of expiration. The use of calendar spread is relevant in cases where it becomes sluggish, and the price of the asset is practically not changed.
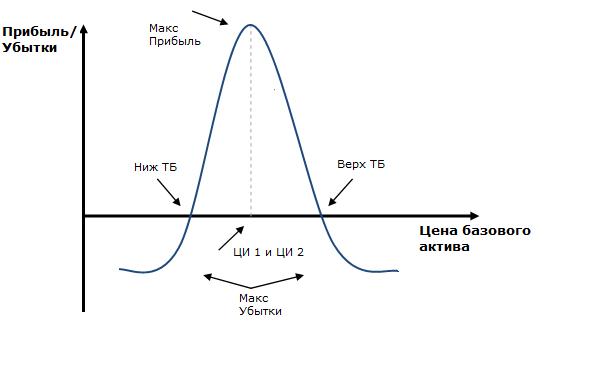
For example, a calendar spread may consist of an already implemented CALL option with the cost of execution 60 and the expiration date, which comes only in a month, as well as a purchased Call option with the cost of execution 60, but expirates the expiration period coming in six months. The implementation of such a strategy makes it possible to finance the LONG position on the asset of interest with minimal price increase.
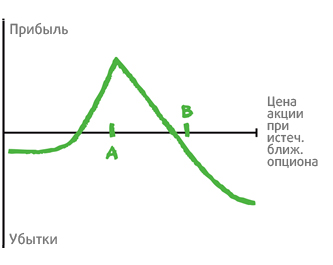
2. Diagonal spread.
The feature of the option strategy is the presence of one short and one LONG of an option with various strikers and expiration period. An example of such a strategy is the implementation of the Call option with the price (strike) 65 (with expiration date after 1 month), as well as the purchase of the Call option, but with another strike (70) and the expiration date after 3 months. As a result, the total price of the diagonal spread is less than, thanks to the higher cost of the optional Call Contract. As for the break-even point, it is located higher than for the calendar spread. As a result, risks will also be higher.
3. Proportional spread.
The strategy is based on coverage of the acquired option contracts at the expense of the award from the options implemented. As an example, you can buy a contract Call or Put, as well as simultaneous sale of options, but with a condition of their lower or high performance price.
The main disadvantage of the strategy is the fact that with a sharp change in the price of the Strategy direction, the option holder turns out to be partially uncovered short position on the contracts already sold.
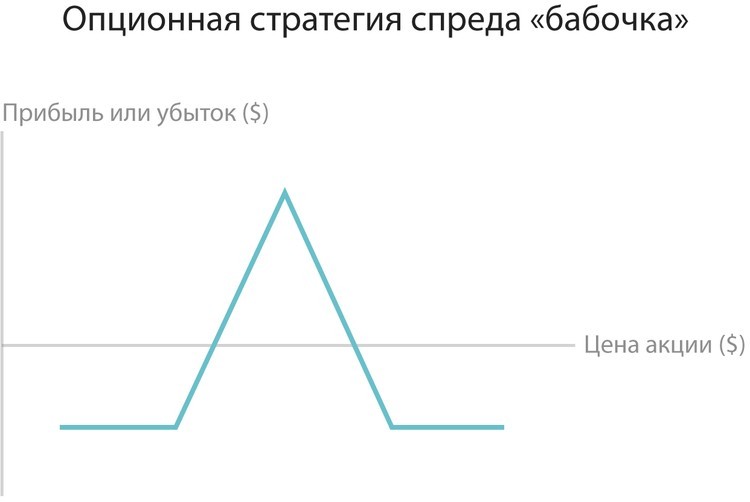
4. Butterfly.
The strategy helps to receive income from transactions with options during periods of lack of trend in the price of the asset. For example, the calculations showed that the price of the instrument will not be released for certain limits. In this situation is bought Strong. At the same time, it is necessary to insure the optional contracts sold. To do this, buy Strangl, which allows you to form a "butterfly" figure on the chart. For example, if the price range is at 50-60 US dollars per asset, then you can sell 55 stranded and at the same time buy 60-50 Strangl.
5. Albatross (iron butterfly).
Such a strategy in its essence and principles of implementation is similar to the option strategy that is previously described. The difference is to apply one direction of the market. For example, when buying one option Call per share, having a strike 60, the investor sells a pair of Call options with the cost of execution 70, and also buys one Call option with Straight 80. All optional contracts that are used in strategy are used alone. This approach allows you to hardly limit risks, and partially finance sales.
6. Christmas tree.
In this strategy, the option contracts "agreed" sold and acquired options having one execution date and one type. For example, if the stock price is 55 dollars, then the investor buys Call with a similar strike (55) and implements two option Call with a large strike (for example, 60), and also buys three call option with Straight 65 and so on. As a result, each "tier" christmas trees will be higher.
Strategies options There are simple and complex. Simple include: the usual purchase / sale of collov / ways, all sorts of species, Strangals and Stradela. Complex strategies include: Butterfly, Condor ,. In this article, we will consider the usual purchase and sale of Call and Put options, as well as all major spreads (direct, proportional, inversely proportional).
Strangle, Streddle, Condor and Butterfly will be described in. Calendar spreads are considered separately. Those or other strategies options Applied depending on what market movement, what the development of the Events expects a trader in the near future.
All optional strategy discussed below were built using the program, in Figure further presents a detailed description of all numbers on the chart (with the goal so that every time you do not march them on the schedules of strategies).
Simple strategies options
The most trivial option strategies is the usual purchase or sale of one option (Call or Put). Buying an option call you expect that the price of the basic asset will grow; Buying a way-option You assume that the Ba price will fall. If you buy any option, then for you the income function will look like the shown in the figure below.

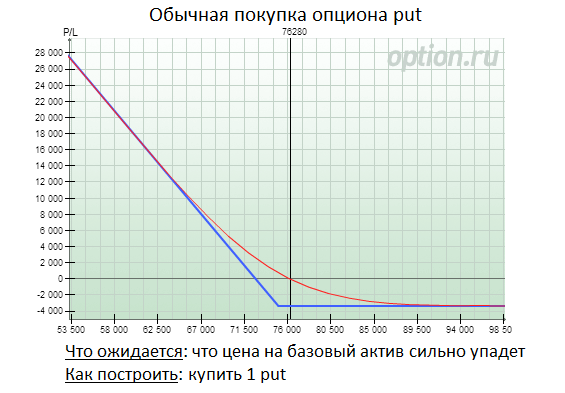
It comes out, the risk of the buyer (call or confuse) is limited only by the sum, i.e. Lose more than the size of the premium paid, the option buyer will not be able. But its income is potentially implanious and actually depends on the possibility of price move in one direction as part of some time interval.
Option strategies are simultaneous, and often combine the purchase or sale of one or more options that differ in one or more variable. Often it is done to enhance impact on a certain type of opportunity or risk, eliminating other risks as part of a trading strategy. Literally, the strategy can simply buy or sell one option, but optional strategies often combine the simultaneous purchase and or sale of several options.
Optional strategies make it possible to make profits from trends such as bullish, bearish or neutral. In the case of neutral strategies, they can be divided into those that are bullish with volatility and those that adhere to bear positions during volatility. The optional positions used can be long and / or short positions in call-options.
Bullish strategy options
Bull and options strategies work when an option trader expects stock prices or other assets to move up. It is necessary to evaluate how high the price of assets and time frames can go, in which this will occur in order to choose the optimal trading strategy.
The most bullish of trading strategy options is a simple Call-options strategy that is used by most starting option traders.
Shares rarely grow not by day, but by the hour. Moderately bullish option traders typically set the target price and use bullish spreads to reduce costs. (True, it does not reduce the risk, because the option may still end with anything.) Although the maximum profit is limited to these strategies, they are usually less expensive in case of failure when used for this nominal number of investments. Bull Call-spread and bullish Put-spread are examples of moderately bovine strategies.
Soft bull trading strategies - These are optional strategies that make money while the basic share price does not fall to the expiration date of the option. These strategies as such can provide a small risk protection. Inscription of moneyless Call options is good example Such a strategy.
Bear strategies options
Bear strategies options work when the option trader expects the stock price to move down. It is necessary to evaluate how low the price of shares can go and a temporary framework in which the decline will occur in order to choose the optimal trading strategy.
The most bearish from the optional trading strategies is a simple strategy for purchasing PUT-options and is used for most of them beginner option traders.
Prices for shares only occasionally make cool downward movements. Moderately bearish option traders usually set the target price for the expected decline and use bearish spreads to reduce costs. While the maximum profit is limited to these strategies, they are also less costly in case of failure. Bear Call-spread and bearish Put-spread are examples of moderately bear strategies.
Soft bearish shopping strategies are optional strategies that make money until the price of the action rises to the expiration date of the option. These strategies as such can provide a small risk protection. In general, bearish strategies give less profit with a smaller risk of losses.
Ordinary or non-directional options strategies
Conventional Options Trade Strategies are used when an option trader does not know whether the basic shares will grow or fall. They are also known as non-directional strategies, and are named because in this case the potential profits does not depend on whether the basic stock price will go up. Rather, the correct use of a neutral strategy depends on the expected volatility of prices for shares.
Examples of neutral strategies are:
Gats. - Sell ITM (in money) Put and Call.
Butterfly - Buy ITM (in money) and OTM (free of money) Call-option, sell two ATM option (about money), or vice versa.
Stredl - keep positions both in Call and in PUT options with the same cost of execution and expiration period. If the options were purchased, the owner has a long stranded. If options were sold, the owner has a short stroke. A long stranded is beneficial if the price of the basic asset varies significantly, above or lower. The short strand is beneficial when there are no such significant changes.
Stranng - Simultaneous purchase or sale of a PUT-option is out of money and a call-option is out of money, with the same expiration date. As in a stroke, but with different prices of execution.
Turn risks - Models the motion of the base price, so sometimes it is called synthetic long or synthetic short positions, depending on which position you close.
Collar - Buy a basic asset, and then simultaneously buy a PUT-option below the current price (Floor) and sell a call-option above the current price (CAP).
Fence - buy a basic asset, and then simultaneously buy options on both sides of the price to limit the range of possible returns.
Iron butterfly - Sell two overlapping credit vertical spredes, but one of the vertical spreads is on the side of Call, and the other is on the PUT side.
Iron Condor - Simultaneous purchase of PUT Sprord and Call spread with the same expiration date and four different execution prices. The iron condor can be considered as a sale of Strangl, instead of buying and limiting the risk both on the Call side and on the PUT side by building a bull vertical PUT of the spread and a bear vertical Call Sprord.
Jade Lizard - Create a bull vertical spread using call-options, with the addition of a purchase of a PUT-option for execution price lower than the Call-Spread version in the same execution cycle.
Bullish optional volatility strategies are neutral trading strategies that brought by the volatility by grace profit when the basic share course carries out significant oscillations up or down. They include a long strled, long stringle, short edge and short butterfly.
Bear optional strategies for volatility are common trading strategies that bring profit to the volatility, when the main campaign is practically no movement. Such strategies include a short strokel, short stringle, ratio of spreads, long edge and long butterfly.
Optional spreads
Optional spreads are the main construction blocks of many options trading strategies. The spreading position is introduced by the purchase and sale of an equal number of options for the same class on one base asset, but at different prices of execution or the deadlines of their expiration.
Three major spread classes are horizontal spread, vertical spread and diagonal spread. They are grouped by the relationship between the cost of execution and the expiration date of the options involved.
Vertical spreads, or cash spreads, are spreads with the participation of options of the same basic asset, the same month of expiration, but with different costs of execution.
Horizontal, or calendar spreads, or temporary spreads are created using the options of the same basic asset, the same performance price, but with different expiration time.
Diagonal spreads are built using the options of the same basic asset, but different pricing prices and validity period. They are called diagonal spreads, because they are a combination of vertical and horizontal processes.
Call and Put spreads. Any spread that is built using call-options can be attributed to Call Sprords, while PUT spread is built using PUT-options.
Bull and bear spreads. If the spread is designed to make a profit from the increase in the price of the basic asset, then this is a bullish spread. Bear Sprord is a spread that implies a favorable outcome when the price of the basic asset is down. Credit and debit spreads. If the premiums sold options are higher than the premiums of the acquired options, then a clean loan will be obtained when entering the spread. If on the contrary, then debit. Spreads that are entered into debt are known as debit spreads, while those who received loan are known as credit spreads.
Combinations of spreads. Many option strategies are built around spreads and combinations of spreads. For example, bullish put spread is derived from a bullish spread, but also is a credit spread, while the iron butterfly can be broken down at combinations of bovine PUT spread and the Bear Call. Sprord.
Briefly about the most important trading strategies Options.
Option is a contract for which the buyer gets the opportunity, but not a commitment to make a purchase or Sale asset At a predetermined price in a certain agreement, a moment in the future or throughout a certain period of time. This feature is worth the money and is called a premium for the option. And this opportunity can be traded.
Traders often begin to carry out transactions with options, insufficiently understanding what optional strategies to them are available to limit risks and maximizing profits. We recently reviewed the basic concepts of this tool in the article "How Options are arranged." We present to your attention 10 simple strategies that will help quickly understand the options as in trading instruments and teach the benefits of their flexibility in trade. Each strategy is illustrated by a schedule, which shows the change in profit or loss from the investor actions depending on the price of the basic asset.
1. Covered call
Instead of buying a uncovered call option, a trader can purchase a base-covered call, that is, to use the "Buying Asset and Sale of Call" ". This strategy implies that you acquire any asset and at the same time sell a call option on it. The size of the acquired asset should be equal to the size of the call option. Investors often use such an approach in short-term operations, expecting a neutral dynamics of the asset price and wanting to earn additional profits in the form of an option premium. They also use this strategy as protection against the potential reduction in the value of the asset.
2. Married Put.
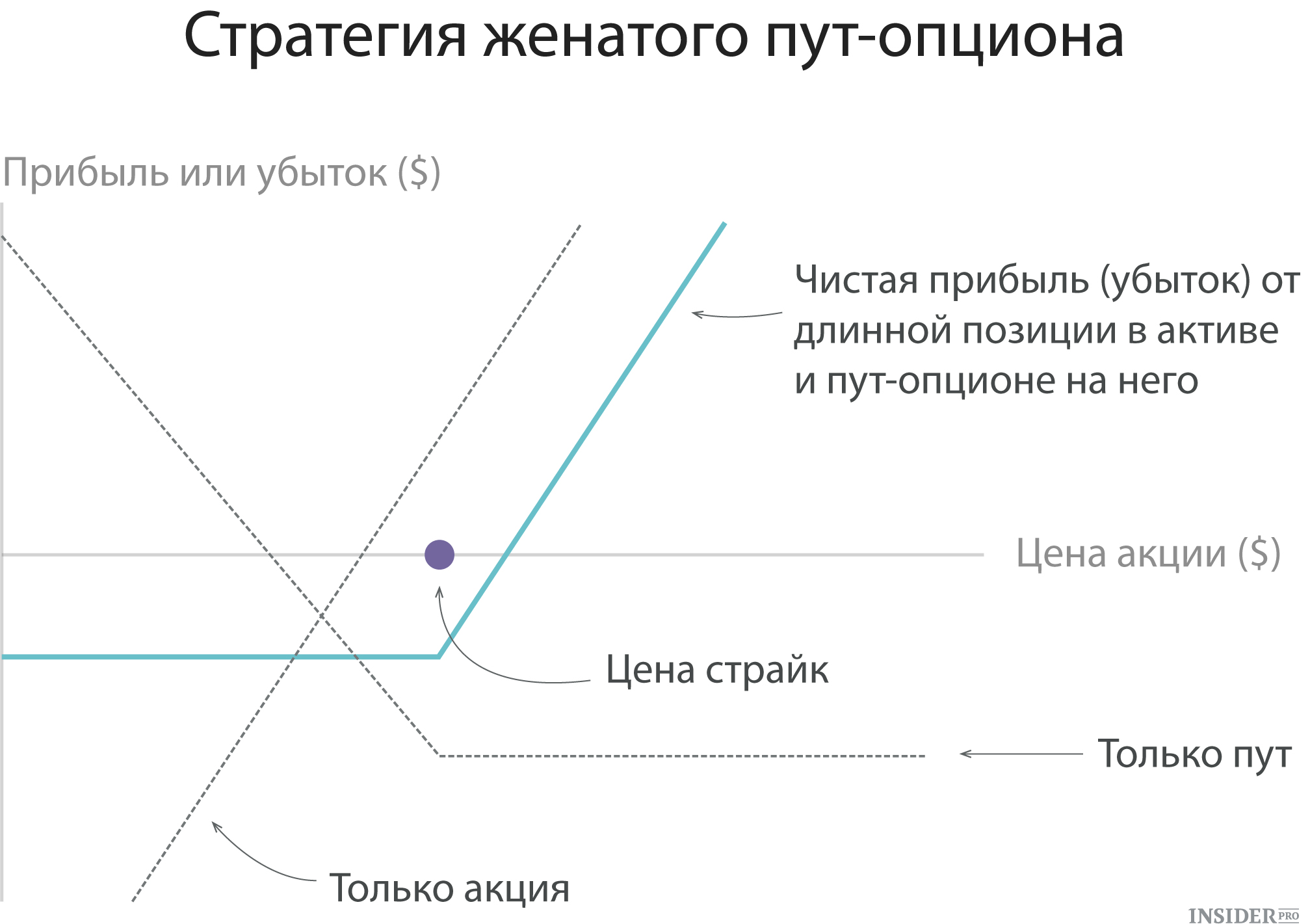
According to this strategy, an investor who acquires or already owning a certain asset (for example, shares) immediately buys up an option for a similar amount of shares. Investors use this approach if they have a "bullish" attitude towards the future stock price and they want to protect themselves from potential losses associated with short-term decrease in quotes. The strategy actually plays the role of insurance and establishes a loss limit with a strong fall in stock price.
3. Bull Call Spread
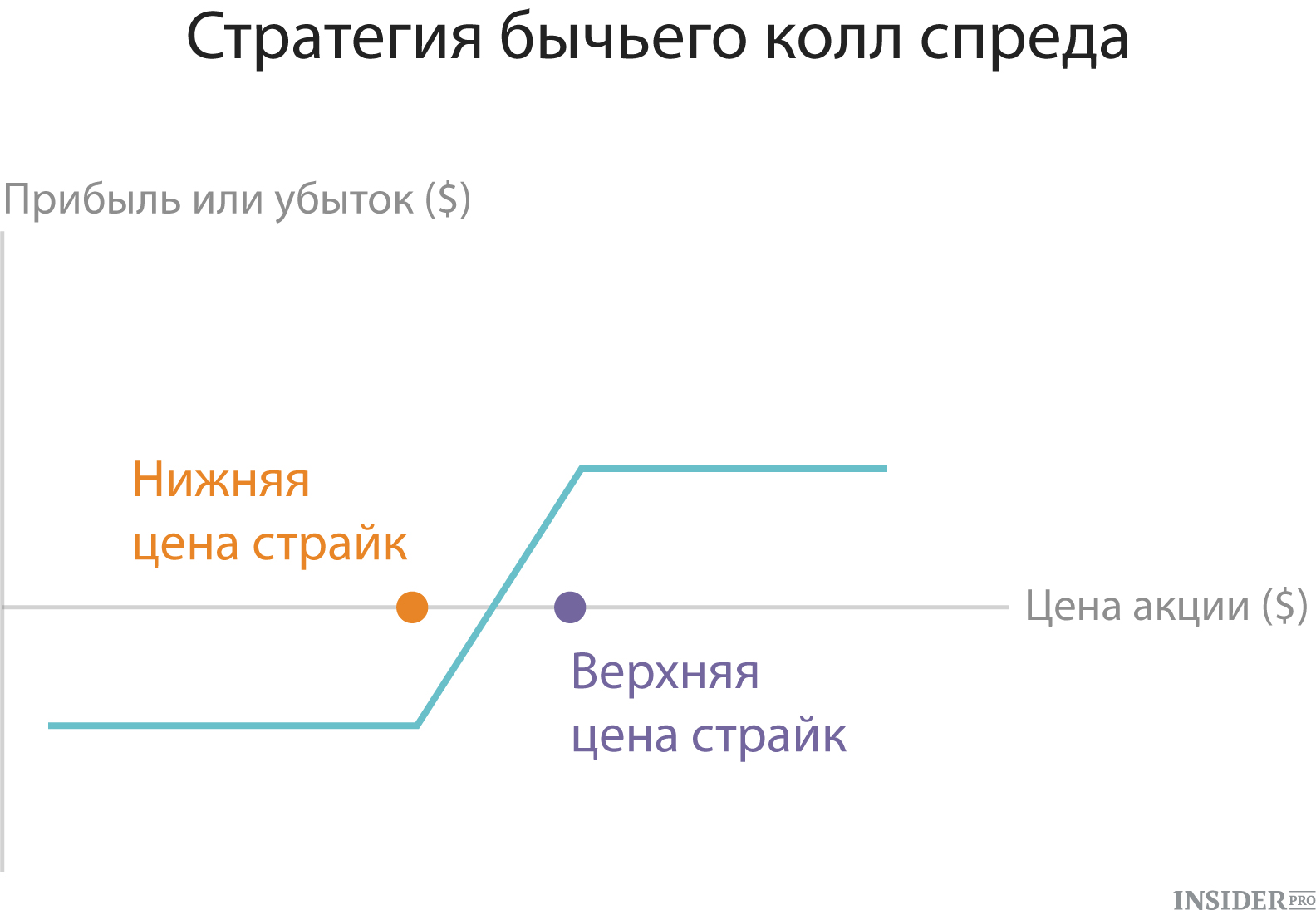
In this strategy, the investor buys call options with a certain strike and at the same time sells the same number of call options with a higher strike. Both call options should be open to the same asset and have the same expiration date. This version of the strategy of the vertical spread is often used in situations where the investor has a bullie and expects a moderate increase in the asset price.
4. Bear Put Spread
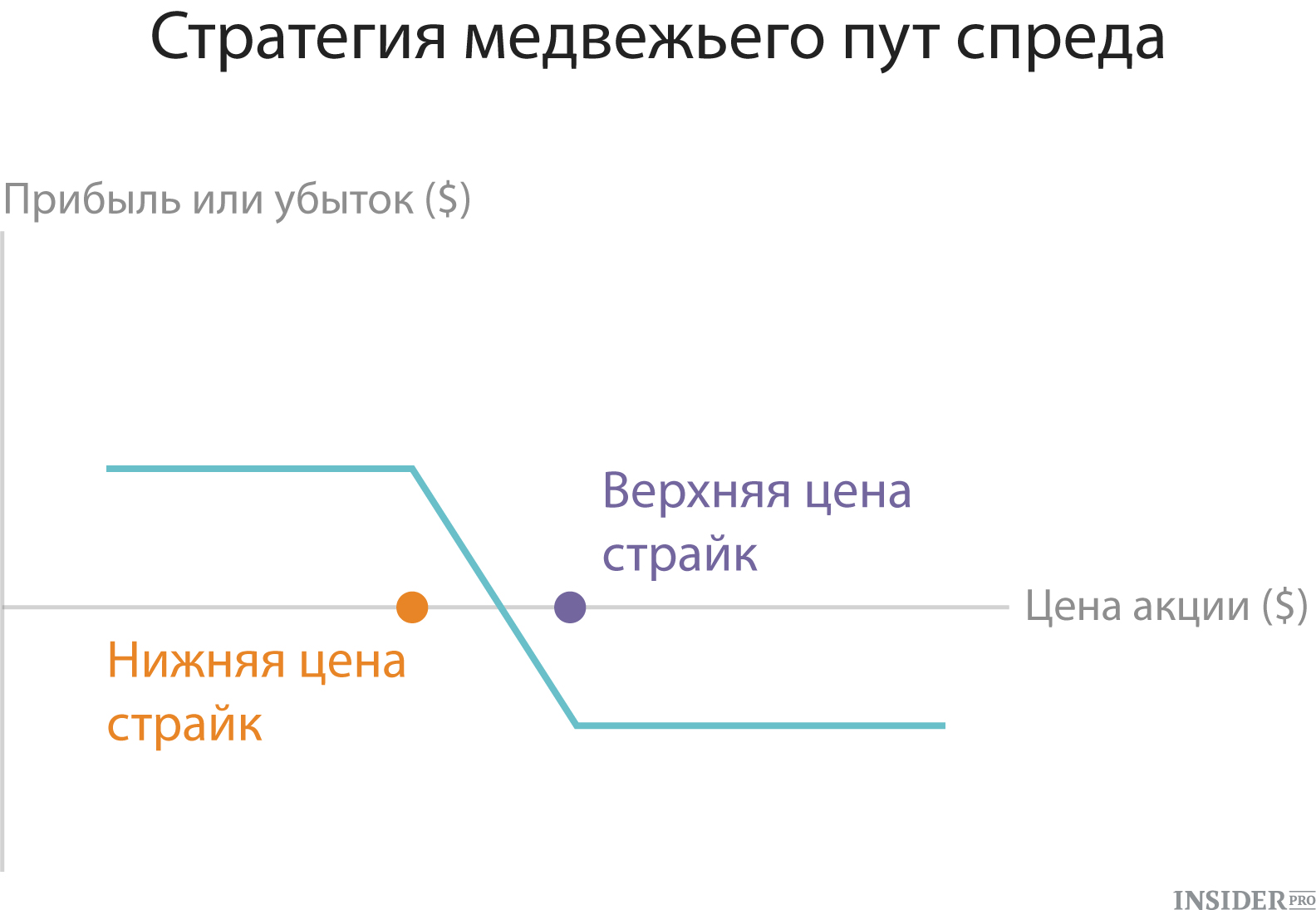
This is another kind of strategy of the vertical spread. In this case, the investor buys up options with a certain strike and at the same time sells the same number of ways with a lower facet. Both options must be open to the same asset and have the same expiration date. This method is used by traders, bearly tuned with respect to the asset and waiting for its price to reduce its price. The strategy allows you to get a fixed amount of profit or loss.
5. Protective collar
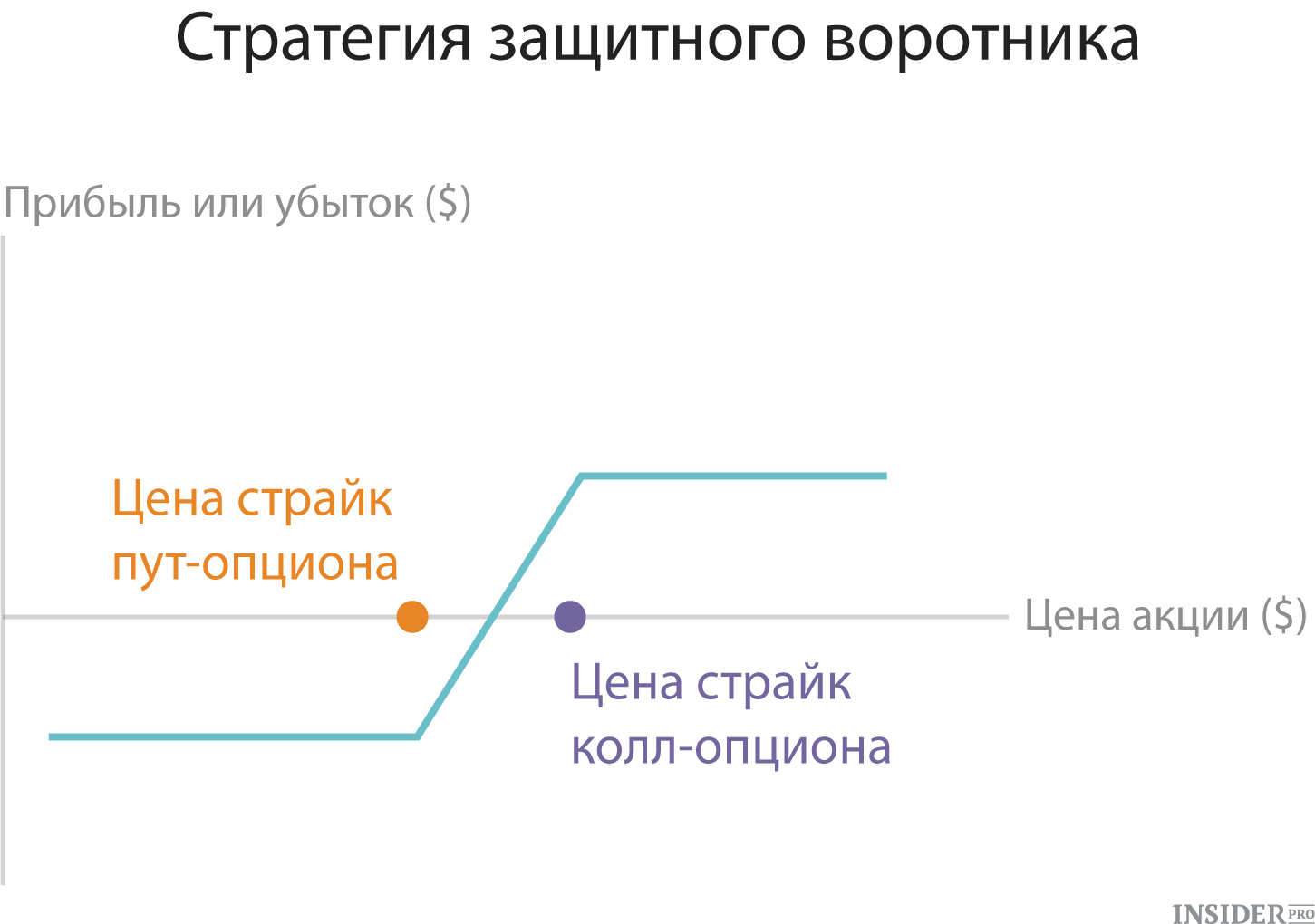
This strategy involves the purchase of an out-of-the money "out-of-the money) and the immediate sale of a call option" off-money "on the same asset (for example, shares). This method is popular among investors who are in Long position And already earned a significant profit. So they can fix profits without selling stocks.
7. Purchase of double option Strangl
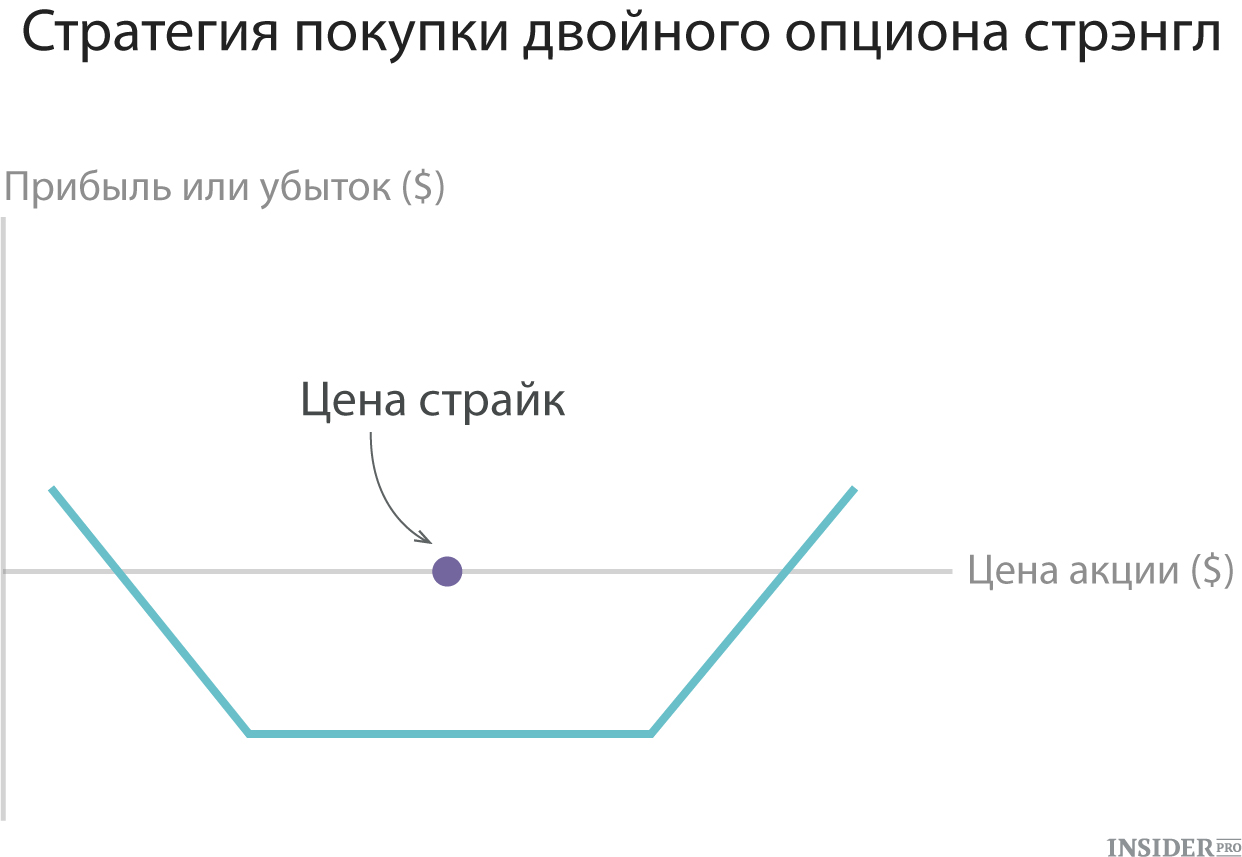
According to this method, the investor acquires a call option and put-option for one asset and with the same expiration date, but different strikes. Typically, the strike price of the way below the side of the collars and both option are "out of money." A trader that uses this strategy expects a strong movement of the asset price, but not confident in the direction of this movement. Losses are limited to the costs of two options, but Strangals are usually less costly than strleddla, since options are bought off "out of money".
By the price of a page with short positions on two different Strategies Strangl. it complex methodrequiring time to teach working with him, as well as the acquisition of experience in its application.
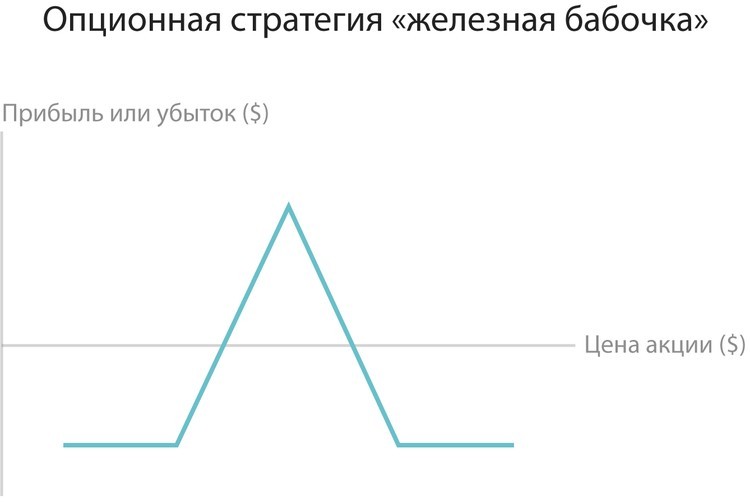
10. "Iron Butterfly"
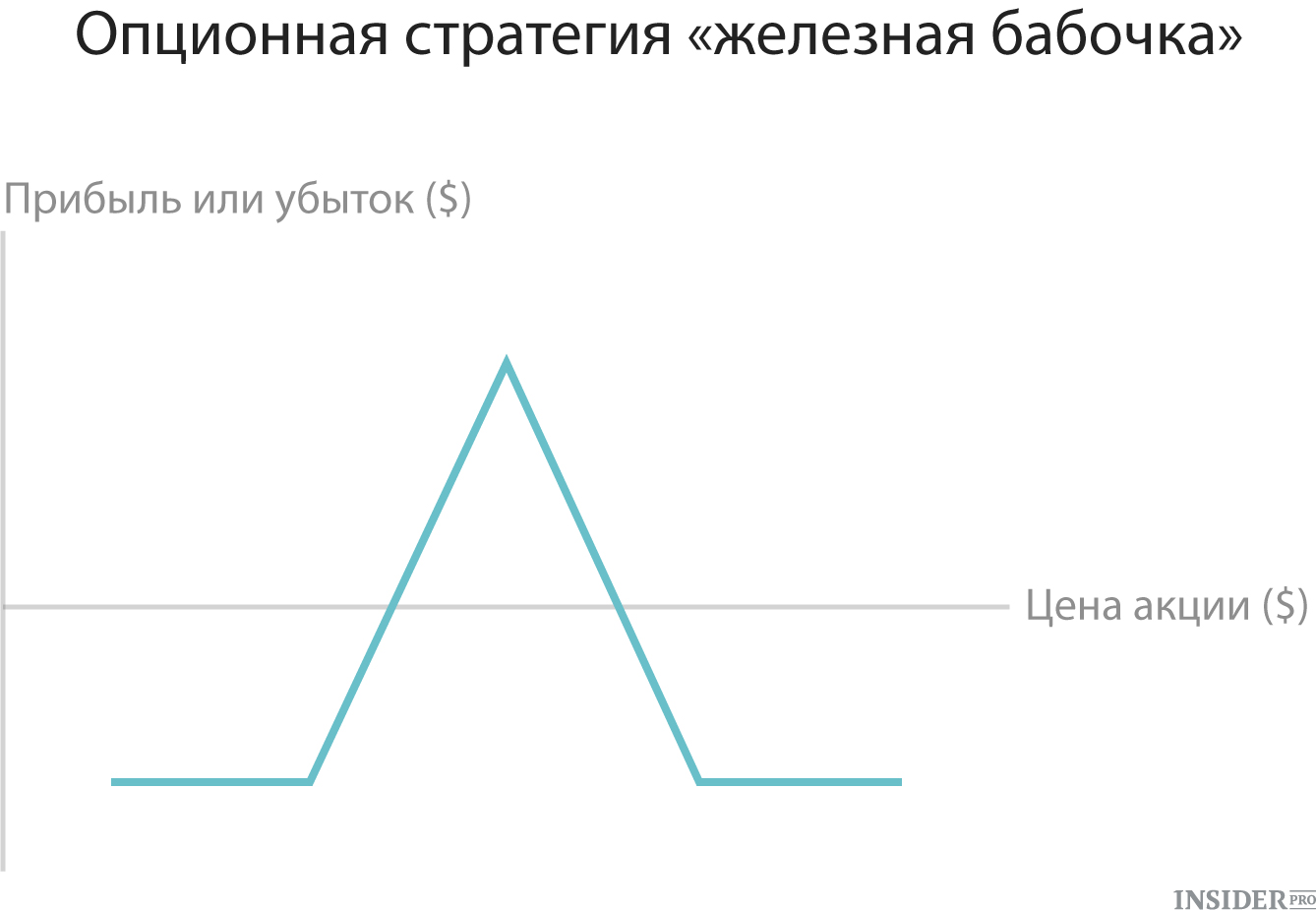
The final example of the strategy is the "iron butterfly". This method suggests that the investor combines the purchase or sale of Stradela with simultaneous purchase or sale of Strangl. Despite its similarity with the strategy of the "Butterfly" spread, there is a difference: in the spread or calls were applied, or in the "iron butterfly" simultaneously use the colts, and the way. Profit and losses of this strategy are limited to a certain interval depending on the strikes of the selected Options. To reduce costs and limit the risks of this method, investors often use




